The history of science is a tapestry woven from revolutionary ideas, and at Top 10 Most, we believe the truly influential theories are those that not only explain the world but fundamentally change how we interact with it. As of late 2025, the global scientific landscape is driven by breakthroughs in computation, genetics, and cosmology, all built atop a bedrock of established, paradigm-shifting concepts.
The theories presented here are not merely historical footnotes; they are active, predictive frameworks that inform everything from the search for gravitational waves and the development of quantum computers to modern medicine and environmental policy. Their influence is measured by their breadth of application, their predictive power, and their ability to withstand generations of scrutiny and testing.
Our ranking is based on a reasoned analytical perspective, prioritizing impact across multiple disciplines and the sheer scale of their intellectual revolution. From the vastness of the cosmos to the inner workings of the atom, these ten theories represent humanity’s most powerful explanations of reality, supported by credible data continuously being verified and refined in November 2025.
Table of the Top 10 Most Influential Scientific Theories
| Rank | Scientific Theory | Originator(s) | Core Concept | Influence Score (1-10) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Quantum Mechanics (QM) | Planck, Bohr, Heisenberg, Schrödinger, et al. | Behavior of matter and energy at the atomic and subatomic level. | 10 |
| 2 | General Relativity (GR) | Albert Einstein | Gravity is the curvature of spacetime caused by mass and energy. | 9.8 |
| 3 | The Theory of Evolution by Natural Selection | Charles Darwin, Alfred Russel Wallace | Biological populations evolve over generations through heritable traits. | 9.5 |
| 4 | The Cell Theory | Schleiden, Schwann, Virchow, et al. | All living organisms are composed of cells, the basic unit of life. | 9.2 |
| 5 | Plate Tectonics | Alfred Wegener, Holmes, Hess, et al. | Earth’s lithosphere is divided into tectonic plates that move. | 9.0 |
| 6 | Classical Electromagnetism | Michael Faraday, James Clerk Maxwell | Electric and magnetic fields are two aspects of a single force. | 8.8 |
| 7 | Newtonian Mechanics/Laws of Motion | Isaac Newton | Describes the relationship between a body and the forces acting upon it. | 8.5 |
| 8 | The Germ Theory of Disease | Louis Pasteur, Robert Koch, et al. | Diseases are caused by microorganisms (pathogens). | 8.3 |
| 9 | Big Bang Theory | Georges Lemaître, Edwin Hubble, et al. | The universe originated from an extremely hot, dense state and has been expanding ever since. | 8.0 |
| 10 | The Laws of Thermodynamics | Sadi Carnot, Rudolf Clausius, et al. | Describes how energy is transferred and transformed. | 7.8 |
Top 10. The Laws of Thermodynamics
The Laws of Thermodynamics are a set of fundamental physical laws that describe how energy is transferred and transformed. At its core, the First Law states that energy cannot be created or destroyed, only converted (conservation of energy), while the Second Law, centered on entropy, dictates that in an isolated system, disorder will always increase over time. These laws govern virtually all processes in the universe, from the internal workings of a star to the efficiency of a steam engine or a computer chip.
The reason for this theory’s enduring influence is its absolute universality. Every piece of machinery, every chemical reaction, and every biological process must adhere to its constraints. As of November 2025, the Second Law in particular is crucial in the pursuit of greater energy efficiency, informing breakthroughs in next-generation batteries, cooling technologies, and the theoretical limits of quantum computing. Understanding the flow of energy is indispensable to modern engineering.
The concept of entropy, as the relentless movement toward disorder, offers a deeply reflective perspective on time and fate within the cosmos. It implies an inevitable “heat death” of the universe, where all available energy is evenly distributed, and no further work is possible. It is a powerful, almost philosophical truth, embedded in the equations that power our world.
Key Highlights:
- First Law: Principle of conservation of energy.
- Second Law: Dictates that the entropy (disorder) of an isolated system always increases.
- Third Law: States that the entropy of a system approaches a constant value as the temperature approaches absolute zero ($0\text{ K}$ or $-273.15^\circ\text{C}$).
- Modern Impact: Crucial for all combustion engines, power generation (e.g., thermal power plants), and optimizing energy systems.
Top 9. Big Bang Theory
The Big Bang Theory is the cosmological model that best explains the earliest moments and subsequent evolution of the observable universe. It posits that the cosmos originated from an extremely hot, dense state approximately 13.8 billion years ago and has been expanding ever since. The empirical evidence for this theory, including the measured expansion of the universe (Hubble’s Law) and the existence of the Cosmic Microwave Background (CMB) radiation, makes it the consensus model for cosmology in November 2025.

Its influence lies in providing a coherent timeline for the cosmos, shifting our understanding from a static universe to one with a distinct origin, age, and future. It sets the foundation for almost all modern astrophysical research, driving the search for dark matter, dark energy, and the first stars. Without the Big Bang framework, contemporary endeavors like the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) would lack the theoretical context to interpret their observations of the deep past.
Perhaps the most powerful aspect of the Big Bang Theory is its ability to quantify the unquantifiable: the beginning of time and space itself. It transformed cosmology from speculative philosophy into a rigorous, evidence-based science. The discovery of the CMB—a faint echo of the universe’s birth—is one of the most remarkable confirmations in human history, offering a direct view into the universe’s infancy.
Key Highlights:
- Core Evidence: Cosmic Microwave Background (CMB) radiation and the observed expansion of the universe (Hubble’s Law).
- Age of Universe: Estimated at 13.8 billion years.
- Future Focus: Research in November 2025 centers on characterizing Dark Matter and Dark Energy, which influence the universe’s expansion fate.
Top 8. The Germ Theory of Disease
The Germ Theory of Disease fundamentally changed medicine by proving that specific diseases are caused by the invasion of the body by microscopic organisms, or pathogens, rather than by “bad air” (miasma) or spiritual imbalances. Pioneered by Louis Pasteur and Robert Koch, this theory established the revolutionary concept that cleanliness and isolation could prevent illness. Before this, doctors often practiced unsanitary procedures, inadvertently spreading infection through contaminated tools and hands.

The immense influence of this theory is evident in global public health and medicine today. It is the direct foundation for practices like sterilization, pasteurization of food, antiseptic surgery, vaccination, and antibiotics. Without the germ theory, modern hospitals, surgical procedures, and the entire pharmaceutical industry would not exist. Its impact during the COVID-19 pandemic reinforced its relevance, guiding protocols for sanitation and disease control in November 2025.
It remains one of the most life-saving scientific theories ever conceived, transitioning humanity from an age where death from common wounds and childbed fever was routine to an era of controlled infection. The simple, yet profound, act of handwashing stands as a monument to the millions of lives saved by the insights of Pasteur and his contemporaries.
Key Highlights:
- Key Practices Derived: Antiseptic surgery, vaccination, pasteurization, and sterilization.
- Verification: Koch’s postulates provide a set of criteria to link a specific microorganism to a specific disease.
- Modern Relevance: The theory continues to guide the development of new vaccines and antibiotics against evolving pathogens in November 2025.
Top 7. Newtonian Mechanics/Laws of Motion
Sir Isaac Newton’s laws of motion and universal gravitation, codified in the 17th century, provided the first unified, mathematical description of the physical world, governing everything from the trajectory of a cannonball to the orbits of planets. Newtonian Mechanics defined concepts like mass, force ($F=ma$), and momentum, introducing a deterministic view of the universe where the future state could, in principle, be calculated from the present state. For centuries, this model was considered the absolute truth of physics.
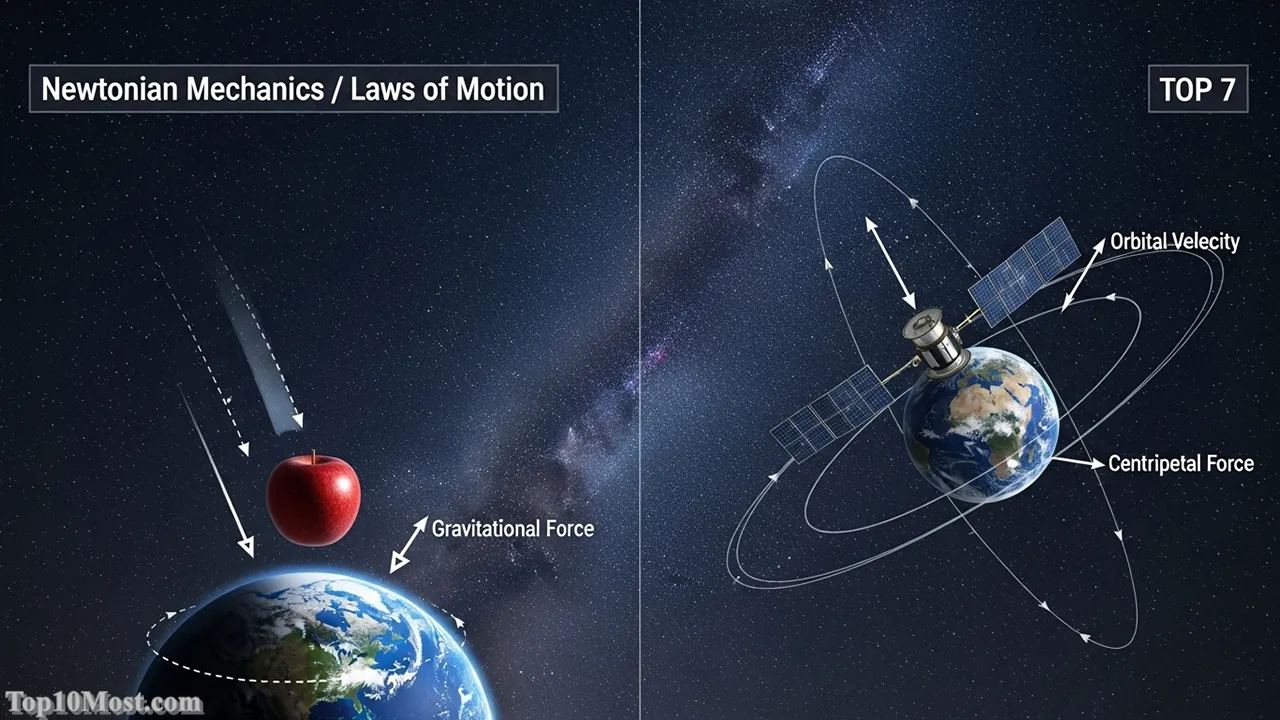
Even though it has been refined by Einstein’s relativity, its influence is still foundational. It remains the operating system for most engineering and classical physics problems today, as its predictions are astonishingly accurate for macroscopic objects traveling at non-relativistic speeds. Every bridge, building, car, and non-GPS satellite in orbit is designed and navigated using Newtonian principles, making it an indispensable tool for practical technology in November 2025.
The revolutionary power of Newton’s work was his ability to use a single set of universal laws to explain phenomena on Earth and in the heavens. This unified approach marked the beginning of modern science, inspiring generations of thinkers to believe that the entire universe was comprehensible through reasoned observation and mathematics.
Key Highlights:
- Core Principle: Three laws of motion ($F=ma$ being the most famous) and the law of universal gravitation.
- Range of Use: Used for virtually all terrestrial engineering and space mechanics (non-GPS orbits).
- Relation to GR: Newtonian mechanics is a highly accurate approximation of General Relativity under weak gravitational fields and low speeds.
Top 6. Classical Electromagnetism
Classical Electromagnetism, primarily formalized by James Clerk Maxwell in the 19th century, unified the previously separate forces of electricity and magnetism into a single, cohesive theory. Maxwell’s Equations showed that light itself is an electromagnetic wave, moving at a constant speed ($c$). This synthesis of light, electricity, and magnetism is considered a triumph of theoretical physics, providing the first glimpse into the interconnectedness of fundamental forces.
Its influence on the modern world is arguably unparalleled in daily life. This theory is the cornerstone of all electrical engineering and electronic technology. Every generator, motor, radio, television, microwave, cell phone, and Wi-Fi signal operates entirely on the principles described by Maxwell. It ushered in the entire age of telecommunications and electricity generation, making it a pivotal force in global infrastructure development right up to November 2025.
Maxwell’s realization that a varying electric field creates a magnetic field and vice versa, leading to the self-propagating electromagnetic wave, was one of science’s most elegant discoveries. It showed that invisible fields of energy permeate space, transmitting information and power across vast distances, a concept that would later inspire Einstein’s work on relativity.
Key Highlights:
- Core Principle: Light is an electromagnetic wave, described by Maxwell’s four equations.
- Key Inventions Derived: All forms of radio, wireless communication, electricity generation, and motors.
- Historical Significance: Unified electricity, magnetism, and light into a single theory.
Top 5. Plate Tectonics
Plate Tectonics is the unifying theory of geology, explaining the movement of the Earth’s lithosphere—the outer crust—which is broken up into giant, shifting plates. This theory explains that continents are not fixed but slowly drift across the globe, driven by convection currents in the underlying mantle. This process is responsible for virtually all major geological phenomena, including earthquakes, volcanoes, mountain formation, and the creation of ocean trenches.
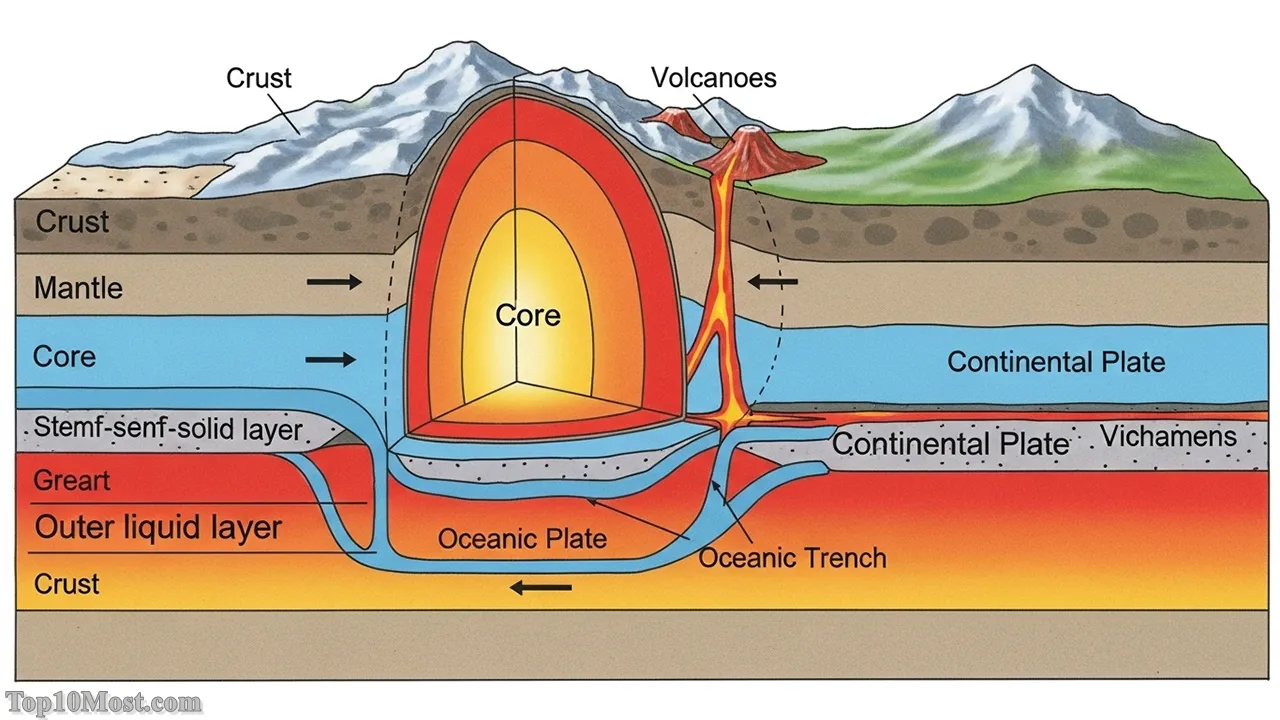
The theory’s influence is profound because it provides a cohesive explanation for the distribution of geological features and the location of natural resources across the planet. It allows scientists to predict seismic and volcanic activity with greater accuracy, informing global disaster preparedness and urban planning. It also provides the framework for understanding climate history and the evolution of life on Earth, cementing its position as a critical planetary science theory in November 2025.
The original idea of continental drift, proposed by Alfred Wegener in 1912, was initially ridiculed for decades until overwhelming evidence from ocean floor mapping and paleomagnetism forced a paradigm shift in the mid-20th century. This history serves as a powerful reminder of how scientific consensus evolves when confronted with robust, undeniable data.
Key Highlights:
- Core Concept: Earth’s lithosphere is made of moving plates driven by mantle convection.
- Phenomena Explained: Earthquakes, volcanic activity, mountain building, and continental drift.
- Foundational Evidence: Seafloor spreading, magnetic striping on the ocean floor, and the alignment of geological features on separated continents.
Top 4. The Cell Theory
The Cell Theory is one of the most essential concepts in biology, establishing that all living organisms are composed of fundamental units called cells, and that all cells arise from pre-existing cells. This simple yet profound realization, formalized in the mid-19th century, provided a universal building block for all known life, from the smallest bacterium to the largest whale. It fundamentally unified botany and zoology under a single structural principle.
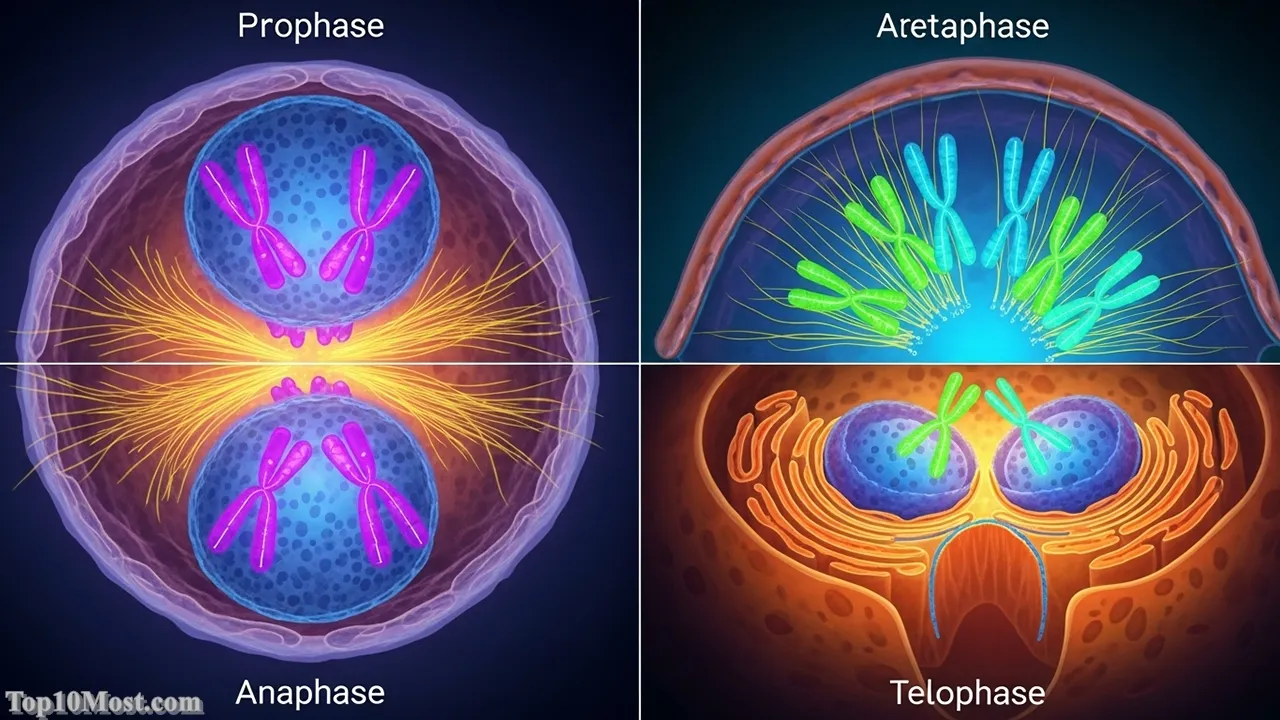
The Cell Theory’s influence is the foundation of virtually all modern biological and medical research. It gave rise to the fields of microbiology, histology, cell biology, and genetics, as it provided the context for understanding diseases, reproduction, and heredity. All major medical breakthroughs in the last century, including vaccine development, cancer research, and gene therapy, are dependent on this concept of the cell as the fundamental functional unit of life. In November 2025, the ability to engineer and manipulate individual cells is the cutting edge of medicine.
The initial resistance to the theory was overcome by the advent of powerful microscopes, which allowed scientists to visualize the cell’s internal structure and division processes. The insight that life begets life at the microscopic level gave science the necessary framework to begin to unlock the incredible complexity of life itself, paving the way for the discovery of DNA.
Key Highlights:
- Three Tenets: All living things are composed of one or more cells; the cell is the basic unit of life; all cells come from pre-existing cells.
- Disciplines Founded: Microbiology, cell biology, and modern genetics.
- Technological Dependence: Requires microscopy to observe and verify the structure and processes of cellular life.
Top 3. The Theory of Evolution by Natural Selection
The Theory of Evolution by Natural Selection, pioneered by Charles Darwin and Alfred Russel Wallace, explains the diversity of life on Earth. It states that biological populations change over successive generations, and that organisms possessing traits better suited to the environment are more likely to survive, reproduce, and pass on those traits. The core mechanism—natural selection—is a simple, mechanistic explanation for the complexity and adaptability of life, without invoking supernatural intervention.

Its influence extends far beyond biology, making it a central pillar of modern scientific and philosophical thought. It is the core organizing principle of the life sciences, informing genetics, ecology, medicine (especially antibiotic resistance), and even anthropology. In November 2025, the theory is continuously strengthened by advances in genomics, which allow scientists to trace evolutionary relationships with unprecedented accuracy, guiding biodiversity conservation and understanding disease transmission.
Evolution offers a profound narrative of deep time, revealing that all life on Earth shares a common ancestor, a realization that forever altered humanity’s place in the universe. It remains a unifying, powerful concept, inspiring awe at the slow, cumulative power of non-random survival acting on random mutation, constantly shaping the living world around us.
Key Highlights:
- Core Mechanism: Natural selection—differential survival and reproduction of individuals due to differences in phenotype.
- Modern Synthesis: The combination of Darwinian evolution with Mendelian genetics.
- Current Application: Explains antibiotic resistance, viral evolution (e.g., SARS-CoV-2 variants), and guides conservation biology.
Top 2. General Relativity (GR)
Albert Einstein’s General Relativity (GR) is a revolutionary theory of gravitation, superseding Newton’s model by describing gravity not as a force acting across space, but as a direct consequence of mass and energy warping the fabric of spacetime. This conceptual leap recast the universe in geometric terms: objects, like planets, follow the shortest path (a geodesic) through this curved spacetime. It is the physics of the very large, governing the structure of the cosmos, the dynamics of galaxies, and the behavior of black holes.

The influence of GR is profound and practical. It is the fundamental theoretical basis for the Global Positioning System (GPS), as the extreme gravitational effects near Earth must be accounted for to maintain the high precision required for navigation. Without GR’s corrections, GPS coordinates would drift by several miles per day. In November 2025, it continues to drive astronomical research, confirmed by the discovery of gravitational waves (ripples in spacetime) and the imaging of black holes.
GR represents a monumental shift in human thought, merging space and time into a single entity. The theory is elegant, mathematically beautiful, and consistently proven correct in the most extreme cosmic environments, making it one of the most powerful and counter-intuitive accomplishments of theoretical physics.
Key Highlights:
- Core Concept: Gravity is the curvature of spacetime caused by mass and energy.
- Practical Application: Essential for the precise operation of the Global Positioning System (GPS).
- Modern Confirmation: Verified by the observation of gravitational lensing, the precession of Mercury’s orbit, and the detection of gravitational waves.
Top 1. Quantum Mechanics (QM)
Quantum Mechanics (QM) is the most influential scientific theory, as it describes the physics of the extremely small: the behavior of matter and energy at the atomic and subatomic level. Its key, counter-intuitive concepts include quantized energy levels, the wave-particle duality, and the uncertainty principle. Unlike classical physics, QM is fundamentally probabilistic, dealing not with certainties but with likelihoods, forcing a radical re-evaluation of the nature of reality itself.
The influence of QM is all-pervasive in modern life, underscoring its top rank. It is the theoretical foundation for the First Quantum Revolution, giving rise to transistors, lasers, and nuclear technology. Every piece of digital technology—from the smartphone in your pocket to the global internet—is dependent on the quantum mechanical understanding of how electrons behave in semiconductors. As of November 2025, QM is fueling the Second Quantum Revolution, which is actively developing quantum computing, quantum encryption (QKD), and ultra-precise quantum sensors, promising to fundamentally reshape computation, medicine, and global security.
QM’s success lies in its staggering accuracy; its predictions are confirmed to an astonishing degree of precision, yet its implications continue to challenge human intuition. It taught science that nature’s basic structure is fundamentally strange and probabilistic, demanding a leap of faith from physicists who nevertheless use its equations daily to engineer the twenty-first century.
Key Highlights:
- Core Concepts: Quantized energy, wave-particle duality, and the Uncertainty Principle.
- First Revolution Products: Transistors (the basis of all modern computing), lasers, and MRI technology.
- Second Revolution Focus: Quantum computing (Qubits), Quantum Key Distribution (QKD) for unbreakable encryption, and ultra-sensitive quantum sensors.
Conclusion
The journey through these ten monumental theories confirms that true scientific influence is not merely about discovery, but about the creation of predictive, robust frameworks that allow for compounding innovation. From the geometric tapestry of spacetime in General Relativity to the probabilistic weirdness of Quantum Mechanics, these concepts represent humanity’s greatest collective explanations of reality. The profound impact of these theories, particularly the continued development of quantum technologies and the genomic applications of evolution and cell theory, underscores their critical importance in November 2025.
At Top 10 Most, we see these theories as living documents, constantly tested and refined by every new experiment and observation. They are the scaffolding upon which the next generation of Nobel Prizes and technological revolutions will be built, reminding us that while the facts are always changing, the foundational principles that explain the meaning behind the greatness remain the most influential of all.