The field of biology has never moved faster than it is in late 2025. What were once concepts confined to science fiction—like curing genetic diseases with a single infusion, designing novel proteins with a computer, or harnessing the power of a pandemic-era vaccine technology for cancer—are now becoming standard clinical realities. This era is defined by the convergence of molecular medicine and computational power, rapidly moving the focus from treating symptoms to correcting root causes.
The advancements detailed here represent the pinnacle of this revolution. They are not merely lab results but transformative technologies that are reshaping medicine, agriculture, and our fundamental understanding of life’s mechanisms. The breakthroughs in areas like CRISPR-based therapeutics and next-generation mRNA technology, for instance, are delivering durable, life-changing results to patients worldwide, establishing new paradigms for how we approach health.
At Top 10 Most, our analysis confirms that the most important breakthroughs are those validated by clinical milestones and real-world impact. The ranking below reflects the reasoned analytical perspective on which innovations have demonstrated the highest potential for long-term societal and scientific influence, supported by verifiable data current as of November 2025.
Table of the Top 10 Most Important Biological Breakthroughs
| Rank | Breakthrough | Core Technology | Primary Impact/Milestone (Nov 2025) | Projected Long-Term Influence |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Clinical CRISPR Gene Editing | CRISPR/Cas9 (exa-cel, in vivo LNP) | Global approval and successful scaling of exa-cel for sickle cell and $\beta$-thalassemia; successful Phase 1 trials for in vivo cardiovascular gene editing (e.g., ANGPTL3, PCSK9). | Curing common and rare monogenic diseases; permanent correction of widespread conditions like high cholesterol. |
| 2 | AI-Accelerated Drug Discovery (AlphaFold) | Generative AI, Deep Learning, Protein Folding | Release and broad adoption of AlphaFold 3 (DeepMind/Isomorphic Labs) for predicting structure and interactions of all life’s molecules; rapid design of novel proteins and antibodies. | Massively reducing drug development timelines and failure rates; enabling design of entirely new classes of therapeutics. |
| 3 | Next-Gen mRNA Therapeutics | Modified mRNA, Lipid Nanoparticle (LNP) Delivery | Success of mRNA vaccines beyond COVID-19 (e.g., approved RSV vaccine); Phase 2/3 trials for personalized cancer immunotherapies and prophylactic flu/CMV vaccines. | Personalized oncology; durable treatment for autoimmune and rare genetic diseases via therapeutic protein expression. |
| 4 | In Vivo Base Editing | CRISPR Base Editors (A, C, G, T) | Advancements in LNP delivery and safety/specificity profiles, moving into early clinical trials for common metabolic and cardiovascular disorders. | Ultra-precise, permanent genetic correction without creating double-strand DNA breaks, significantly reducing off-target risks. |
| 5 | Multi-Omics and Spatial Biology | High-throughput sequencing, Mass Spectrometry, Imaging | Integration of genomics, proteomics, and transcriptomics with spatial context to map cell interactions in tumors and tissues. | Unprecedented understanding of disease microenvironments; highly refined diagnostics and targets for precision medicine. |
| 6 | Allogeneic (Off-the-Shelf) Cell Therapy | Gene-edited iPSCs, NK and CAR T-cells | Successful Phase 1/2 trials for allogeneic CAR T-cells in blood cancers and early trials for stem cell-derived beta islet cells for Type 1 Diabetes (T1D). | Making complex cell therapies accessible, scalable, and affordable by eliminating the need for personalized patient-derived cells. |
| 7 | Synthetic Genomics and Bio-Manufacturing | Computational Design, Yeast/E. Coli Factories | Engineering of microbial strains for sustainable bioproduction of complex molecules (e.g., biofuels, rare cannabinoids, novel antibiotics) at industrial scale. | Sustainable, bio-based alternatives to petrochemicals; rapid response manufacturing for pandemics and resource scarcity. |
| 8 | Precision Microbiome Editing | Phage Therapy, CRISPR-based Antimicrobials | Clinical trials for phage therapy targeting antibiotic-resistant infections; development of CRISPR-Cas systems to selectively remove pathogenic bacteria from the gut. | Overcoming the antimicrobial resistance crisis; targeted modulation of the gut-brain axis for neurological and metabolic disorders. |
| 9 | Organoid and Tumoroid Models (3D Culture) | Advanced Tissue Engineering, Microfluidics | Standardized protocols for creating patient-derived, functional organoids (brain, liver, kidney) for high-throughput drug screening and personalized toxicity testing. | Replacing less accurate 2D models and animal testing; improving the predictability of pre-clinical drug candidates. |
| 10 | Senolytics and Anti-Aging Therapeutics | Targeted drug compounds, Small-molecule delivery | Positive Phase 2 data on compounds selectively clearing senescent (“zombie”) cells to treat age-related conditions like osteoarthritis and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF). | Direct intervention in the biological mechanisms of aging, shifting the focus of healthcare from disease treatment to health span extension. |
Top 10. Senolytics and Anti-Aging Therapeutics
The quest to understand and reverse aging has shifted from fringe science to a foundational biological pursuit, spearheaded by the development of senolytic drugs. This breakthrough targets senescent cells—often called “zombie cells”—which accumulate with age and secrete inflammatory factors that drive chronic disease. As of November 2025, senolytics have moved beyond theoretical models and are showing tangible clinical results in human trials, offering hope that the underlying process of aging itself can be targeted.

The reason for this ranking lies in the mechanism of action and its broad potential impact. By selectively clearing these harmful senescent cells, senolytics have demonstrated the ability to treat multiple age-related conditions simultaneously, including idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) and osteoarthritis, as seen in recent Phase 2 trial readouts. This holistic approach to age-related pathologies represents a fundamental change in geriatric medicine, proposing a way to prevent the cluster of diseases that come with advanced age rather than treating them individually.
This breakthrough is memorable because it is one of the first direct pharmacological interventions to address the biological clock. The reflection here is profound: a successful senolytic therapy would shift healthcare away from lifelong disease management toward a preventative strategy focused on maintaining cellular health and extending not just life, but “health span.”
Key Highlights:
- Clinical Proof: Positive Phase 2 data in specific age-related conditions (e.g., IPF) validate the senolytic concept in humans.
- Mechanism: Selective apoptosis (programmed cell death) of harmful, pro-inflammatory senescent cells.
- Future Scope: Potential to treat the vast majority of age-related diseases from a single biological cause.
Top 9. Organoid and Tumoroid Models (3D Culture)
The ability to grow complex, self-organizing miniature organs and tumors from human stem cells has fundamentally changed the landscape of drug development by late November 2025. These three-dimensional “organoids” and “tumoroids”—often grown in advanced microfluidic platforms—mimic the structure and function of human tissues far more accurately than traditional two-dimensional cell cultures. This superior fidelity is streamlining pre-clinical research and has become a mandatory component for evaluating drug toxicity and efficacy.
This technology earns its place due to its role as a bridge between lab bench and clinic. Patient-derived tumoroids, for instance, allow oncologists to test multiple chemotherapy or immunotherapy regimens outside the body, providing a highly personalized prediction of which treatment will be most effective for that individual patient. Furthermore, regulatory acceptance of organoid data is beginning to reduce the reliance on less predictive animal models, making drug development faster, more ethical, and more human-relevant.
The remarkable detail achievable in these models—down to generating pulsating heart organoids or complex cerebral structures—is the memorable aspect. The reflection is that the organoid breakthrough represents the dawn of “Human-on-a-Chip” biology, where personalized and predictive medicine can be practiced in a dish before ever being administered to a patient.
Key Highlights:
- Fidelity: 3D structure and multicellular complexity far surpass traditional 2D cell cultures.
- Personalization: Patient-derived tumoroids predict drug response with high accuracy in oncology.
- Automation: Integration with microfluidics enables high-throughput screening for drug toxicity.
Top 8. Precision Microbiome Editing
The field of microbiome research has matured beyond simple correlation and is now defined by the ability to precisely edit the microbial communities within the gut, a critical biological environment. By November 2025, this breakthrough includes the resurgence of targeted bacteriophage (phage) therapy against antibiotic-resistant bacteria, as well as the initial clinical translation of programmable CRISPR-Cas systems designed to selectively neutralize or eliminate specific, harmful bacterial strains.
The reason for this breakthrough’s importance is its direct attack on the antimicrobial resistance crisis and its connection to systemic health. The traditional use of broad-spectrum antibiotics—a biological sledgehammer—is being replaced by these highly specific tools, which can eliminate pathogens without damaging the entire, beneficial microbial ecosystem. This precision extends to neurological and metabolic disorders, where targeted modulation of the gut-brain axis is beginning to show therapeutic benefits.
The most powerful reflection is that we are moving from treating infections with a generalized assault to using a biological scalpel. This breakthrough reframes the gut as a powerful therapeutic landscape, using nature’s own tools (phages) and engineering’s most precise instruments (CRISPR) to restore health.
Key Highlights:
- Phage Therapy: Clinical success against multi-drug resistant bacterial infections where antibiotics have failed.
- CRISPR Targeting: Programmable systems allow for the selective removal of pathogenic strains from the gut without collateral damage.
- Systemic Link: Targeted modulation is showing promise in treating systemic disorders linked to the gut-brain axis.
Top 7. Synthetic Genomics and Bio-Manufacturing
Synthetic biology, the engineering of biological systems for utilitarian purposes, has achieved industrial scale by late November 2025, marking a significant biological and commercial breakthrough. Through advancements in computational design and genetic circuit engineering, organisms like yeast and E. coli have been reprogrammed into “bio-factories” capable of sustainably producing molecules—from complex pharmaceuticals to specialty chemicals—that were previously derived from finite or harmful resources. This represents a pivot from traditional chemistry to a bio-based economy.
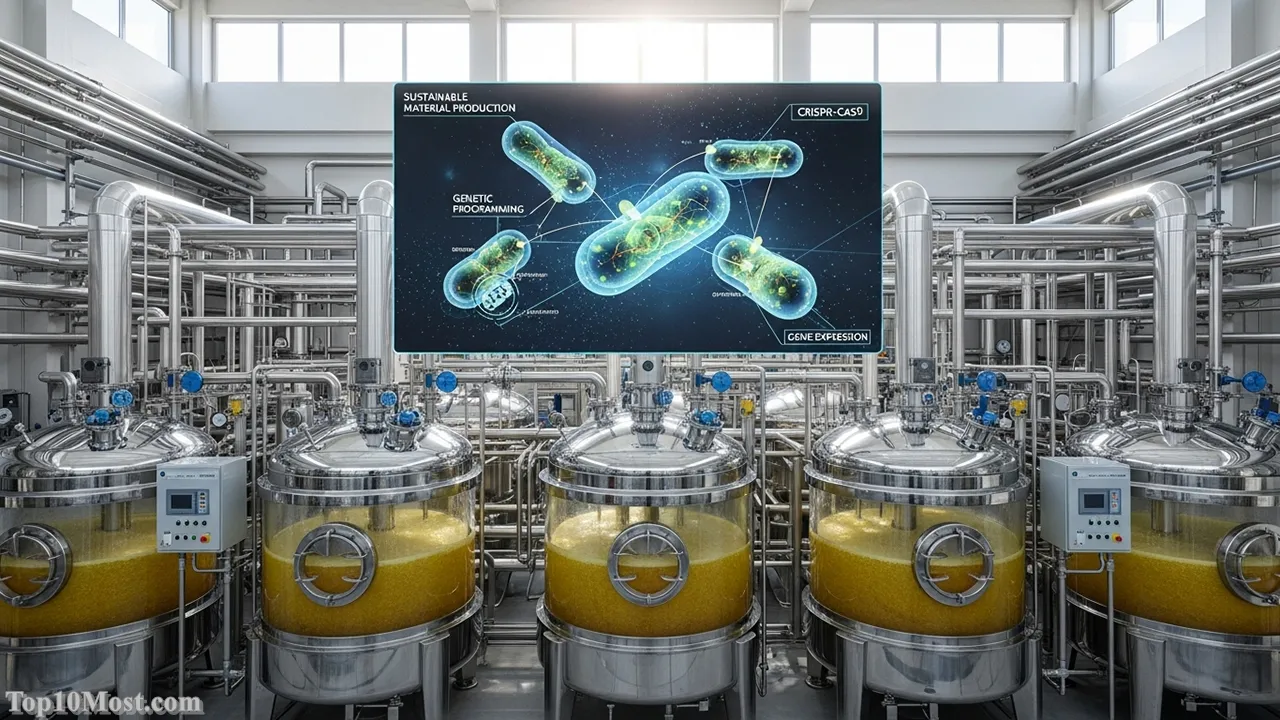

This ranking reflects the technology’s implications for sustainability and supply chain resilience. The ability to use sugar and other renewable feedstocks to manufacture complex products—such as rare cannabinoids, next-generation biofuels, and even novel antibiotics—bypasses volatile supply chains and reduces the environmental footprint of chemical synthesis. This innovation proves that biology can be engineered with the predictability and efficiency of mechanical processes.
The memorable detail here is the sheer complexity of the engineered metabolic pathways. The reflection is that synthetic genomics is not just a scientific field; it is the ultimate green technology. It allows us to design and build biological systems for a cleaner, more sustainable, and resource-independent future.
Key Highlights:
- Computational Design: AI models optimize genetic circuits and metabolic pathways for maximum yield.
- Product Range: Production spans complex drugs, sustainable materials, and industrial chemicals from renewable feedstocks.
- Sustainability: Provides non-petroleum-based, environmentally friendly alternatives for manufacturing.
Top 6. Allogeneic (Off-the-Shelf) Cell Therapy
A major limitation of earlier cell therapies, like the revolutionary CAR T-cells, was the requirement to extract, modify, and reinfuse a patient’s own cells (autologous), making the treatment expensive, slow, and inaccessible. By November 2025, the breakthrough of allogeneic, or “off-the-shelf,” cell therapy has emerged, utilizing gene-edited induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) or other donor sources to create ready-to-use cell products. This technology is fundamentally driven by the use of gene editing to ensure the donor cells are not rejected by the recipient’s immune system.
This breakthrough is highly ranked because it democratizes advanced medicine. By moving from a personalized manufacturing process to a scalable, pharmaceutical-like model, allogeneic therapies dramatically reduce the cost and waiting time for life-saving treatments for cancers and, increasingly, regenerative medicine applications. Early trials for allogeneic CAR T-cells in specific blood cancers and the development of stem cell-derived beta islet cells for Type 1 Diabetes are proving the concept’s viability.
The significance is best seen in the parallel to mass-produced pharmaceuticals. The reflection is that the dream of universally accessible, cell-based cures—where complex biological products are pulled from a freezer and administered immediately—is rapidly becoming a reality, thanks to sophisticated gene and cell engineering.
Key Highlights:
- Scalability: Allows for centralized manufacturing, driving down costs and improving patient access.
- Immune Evasion: Gene editing is used to modify allogeneic cells to prevent host immune rejection.
- Clinical Reach: Showing promise in oncology and, crucially, in regenerative medicine (e.g., T1D).
Top 5. Multi-Omics and Spatial Biology
Biology is no longer analyzed one molecule at a time. The breakthrough in Multi-Omics and Spatial Biology, prominent in November 2025, involves integrating massive datasets—genomics (DNA), transcriptomics (RNA), and proteomics (protein)—and, most critically, mapping them to their exact location within a tissue. This spatial context reveals not just what molecules are present, but how cells communicate, interact, and function in a living microenvironment, especially in complex tissues like tumors or the brain.
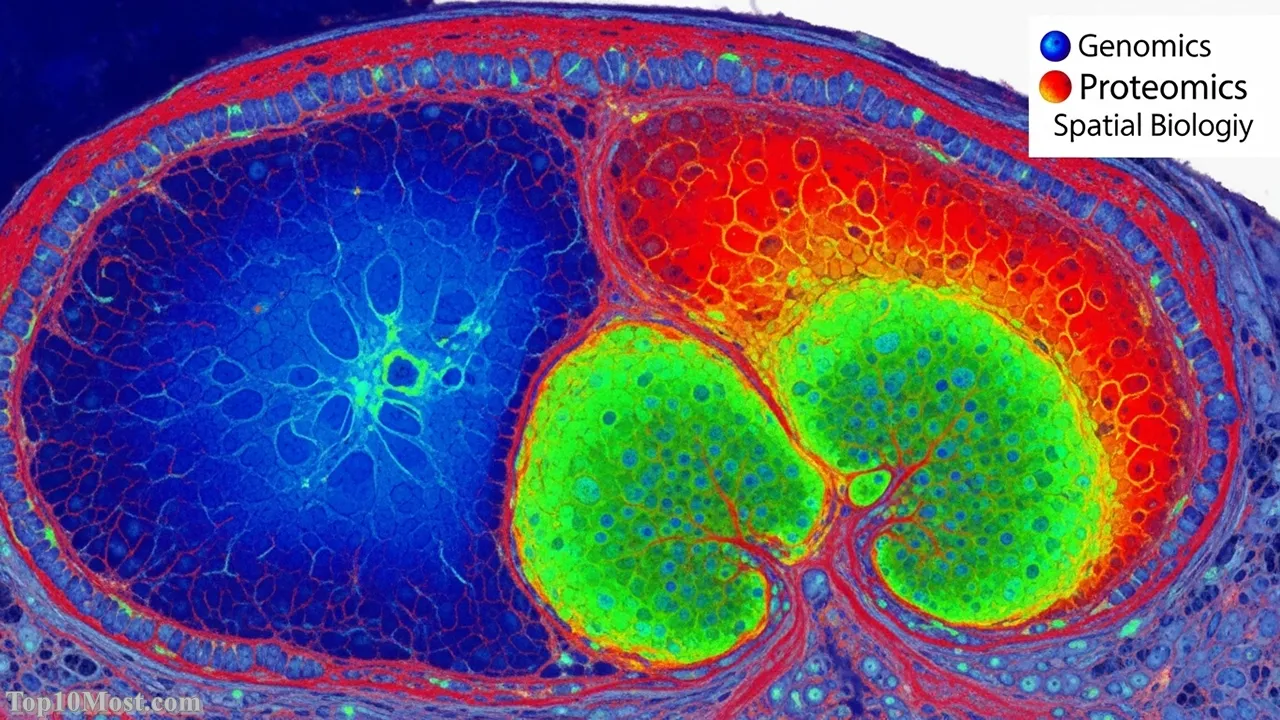
This is a pivotal breakthrough because it unlocks the true complexity of disease. Diseases like cancer or Alzheimer’s are not monolithic; they are highly localized events driven by cell-to-cell communication. Spatial technology provides a ‘Google Earth’ view of pathology, allowing researchers to pinpoint the exact cells, molecular pathways, and interactions driving disease progression. This is leading to the identification of highly refined and previously hidden drug targets for precision medicine.
The memorable feature of this technology is the sheer visualization of life’s processes. The reflection is that the shift from bulk analysis to spatially resolved data is closing the critical gap between molecular biology and physiology, offering a holistic and incredibly detailed picture of health and disease that was unattainable just a few years ago.
Key Highlights:
- Data Integration: Combines genetic, RNA, and protein information into one cohesive, spatially defined map.
- Microenvironment Insight: Reveals crucial cell-to-cell communication within complex tissues (e.g., tumor microenvironment).
- Precision Targeting: Enables the identification of drug targets based on location and interaction, not just presence.
Top 4. In Vivo Base Editing
Base editing, a refinement of the original CRISPR technology, has rapidly become a major breakthrough by November 2025 due to its enhanced safety and precision. Instead of acting as a “genetic scissor” that cuts both strands of the DNA helix (which can lead to unintended large-scale rearrangements), base editors are “genetic pencils” that chemically change one DNA letter (A, C, G, or T) into another without introducing a double-strand break. This ultra-precise editing capability is now moving in vivo (inside the body) using sophisticated lipid nanoparticle (LNP) delivery systems.
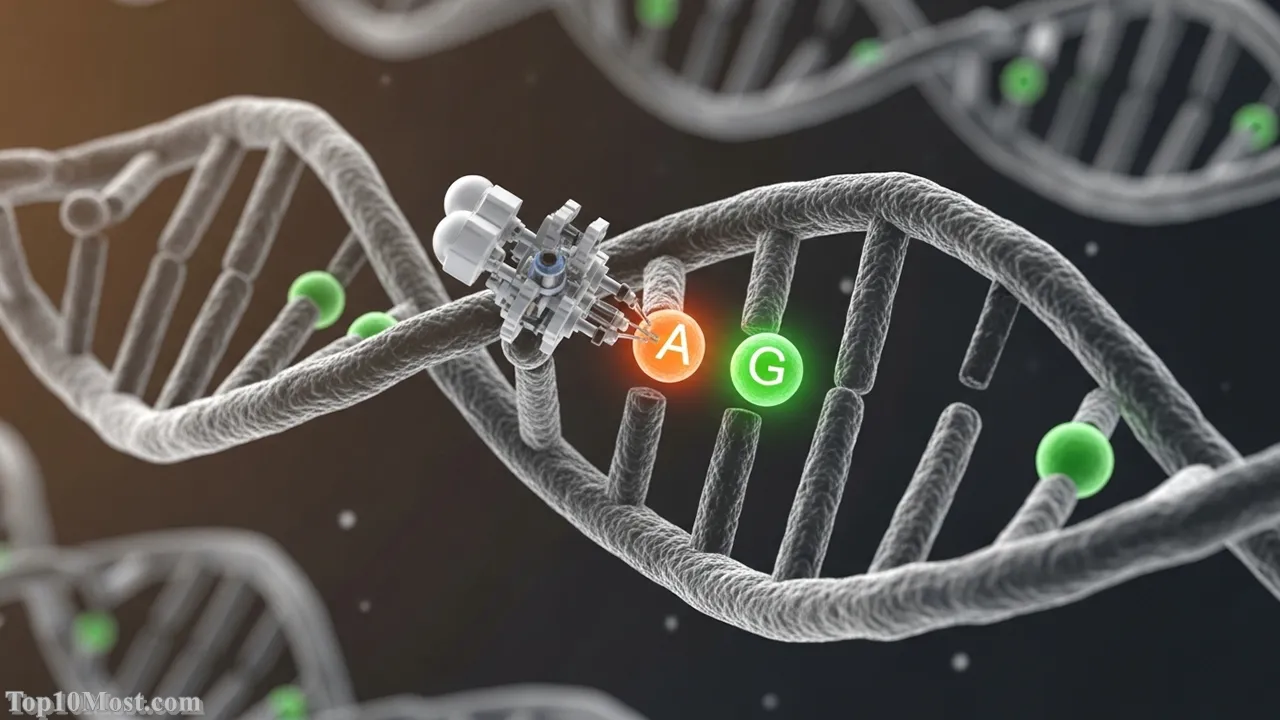

Base editing is ranked highly for its minimal risk profile and expanding clinical utility. Its ability to correct point mutations—the single-letter typos that cause a majority of human genetic diseases—with significantly reduced risk of off-target effects represents a massive leap in gene-editing safety. As seen in early clinical trials for metabolic and cardiovascular disorders, the targeted in vivo delivery of the base editor to organs like the liver suggests a single treatment could provide a lifelong cure for widespread conditions.
The elegance of this technology is its most memorable feature—the ability to perform surgery on a single atom within the genome. The reflection is that base editing is not just an improvement; it is the evolution of gene editing, promising to make genetic correction safer, faster, and applicable to millions suffering from diseases rooted in single-nucleotide mutations.
Key Highlights:
- Precision: Corrects single-point mutations without introducing risky double-strand DNA breaks.
- Safety: Significantly reduces the incidence of large genomic rearrangements and off-target edits.
- Delivery: Progress in LNP delivery facilitates in vivo application to organs like the liver, making it non-invasive.
Top 3. Next-Gen mRNA Therapeutics
While the initial breakthrough of mRNA technology was its use in COVID-19 vaccines, its current evolution by November 2025 is far more expansive, focusing on therapeutic applications beyond infectious disease. Next-generation mRNA platforms now leverage improved stability, novel chemistries, and specialized Lipid Nanoparticle (LNP) delivery systems to instruct the body’s cells to produce therapeutic proteins in vivo. This includes personalized cancer vaccines, durable prophylactic vaccines for common viruses (RSV, CMV), and treatments for rare genetic and autoimmune diseases.

This breakthrough is a top-tier game-changer because of its speed, modularity, and breadth of application. The platform can be rapidly reprogrammed to encode virtually any protein, allowing for personalized cancer immunotherapies that specifically train the immune system to attack a patient’s unique tumor mutations. Furthermore, therapeutic mRNA can be used to treat genetic disorders by instructing cells to produce a missing or defective protein, offering a non-permanent, regulatable alternative to permanent gene therapy.
The most enduring reflection of this technology is its validated global impact and unprecedented adaptability. The success of the mRNA COVID-19 and RSV vaccines proved the platform’s safety and scalability, paving the way for it to become a cornerstone of personalized oncology and a versatile tool for treating chronic, non-communicable diseases.
Key Highlights:
- Personalized Oncology: Phase 3 trials for mRNA cancer vaccines show significant potential when combined with immunotherapy.
- Therapeutic Protein Production: Used to treat genetic disorders and autoimmune diseases by instructing cells to express therapeutic proteins.
- Modularity: Rapid design and production allow for quick pivots to new disease targets or emerging pathogens.
Top 2. AI-Accelerated Drug Discovery (AlphaFold)
The application of Artificial Intelligence (AI), particularly deep learning models like AlphaFold 3 (developed by Google DeepMind and Isomorphic Labs), has created a foundational breakthrough that permeates all of biology by November 2025. This technology can accurately predict the three-dimensional structure and, crucially, the interactions of nearly all molecules of life—proteins, DNA, RNA, and ligands. This capability resolves one of biology’s longest-standing challenges and has fundamentally reinvented the drug discovery pipeline.
AI-accelerated drug discovery ranks second because it is a meta-breakthrough that catalyzes all others. The primary bottleneck in drug development has always been the time-consuming and expensive process of understanding how a potential drug molecule interacts with its biological target. AI drastically cuts down the 13.5-year average drug development timeline and significantly reduces the 80% failure rate by simulating interactions in silico (via computer). This is enabling the rapid design of entirely new, novel proteins and antibodies with specific therapeutic functions.
The defining, memorable aspect of this breakthrough is the transition from slow, painstaking experimentation to instantaneous, accurate prediction. The reflection is that AI is not just a tool; it is the new co-pilot for the molecular biologist, poised to unlock therapeutic solutions for diseases that were previously deemed “undruggable.”
Key Highlights:
- Universal Prediction: AlphaFold 3 predicts the structure and interaction of all biomolecules, not just proteins.
- Pipeline Acceleration: Cuts years and billions of dollars from the pre-clinical drug discovery phase.
- Generative Capability: AI is used to design entirely novel, functional proteins and antibodies that do not exist in nature.
Top 1. Clinical CRISPR Gene Editing
The undeniable number one breakthrough is the transition of CRISPR-Cas9 gene editing from a lab tool to a globally approved and transformative clinical therapeutic by November 2025. The most prominent example is Exagamglogene Autotemcel (exa-cel, known commercially as Casgevy), which received landmark approvals across multiple regions for treating sickle cell disease (SCD) and $\beta$-thalassemia. Concurrently, advancements in in vivo delivery using lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) are showing unprecedented success in early trials for common conditions like hypercholesterolemia, demonstrating that a single infusion can permanently correct a genetic defect.

CRISPR is ranked first because it is the first widely validated technology that offers a one-time, curative solution for genetic diseases. For patients with SCD and $\beta$-thalassemia, exa-cel is not a treatment—it is a functional cure that eliminates a lifetime of debilitating symptoms, demonstrating the ultimate potential of molecular medicine. The ability, as shown in recent November 2025 clinical updates (e.g., CTX310 targeting ANGPTL3), to permanently reduce cardiovascular risk factors with a single, minimally invasive injection into the bloodstream marks the shift of gene editing from rare disease to widespread public health utility.
The most memorable feature is the sheer, audacious notion of editing the human blueprint to eliminate disease. The ultimate reflection is that clinical CRISPR represents the fulfillment of the genetic revolution: we have moved beyond simply reading the code of life to having the power to rewrite it, offering the first true functional cure for what were once lifelong genetic burdens.
Key Highlights:
- First Functional Cure: Exa-cel offers a definitive, one-time cure for sickle cell disease and $\beta$-thalassemia.
- Widespread Utility: In vivo LNP delivery extends application to common disorders like high cholesterol (ANGPTL3 editing).
- Pivotal Moment: Marks the first time a general-purpose, programmable gene editing platform has been clinically and commercially scaled.
Conclusion
The biological breakthroughs witnessed by Top 10 Most in November 2025 confirm that we are in the golden age of life sciences. The common thread running through this top 10 list is the convergence of two powerful forces: the precision of genetic engineering (CRISPR, Base Editing, mRNA) and the exponential power of computational biology (AI, Multi-Omics). This synergy has dissolved the traditional barriers of therapeutic development, transitioning medicine from a reactive discipline of managing chronic illness to a proactive one focused on permanent correction and health extension. The curative nature of clinical CRISPR, the unparalleled foresight offered by AlphaFold 3, and the therapeutic versatility of next-generation mRNA are not just scientific successes; they are a profound promise to humanity that the most challenging diseases may soon be relegated to history.