At Top 10 Most, our pursuit is to encapsulate the sheer magnitude of scientific achievement. Physics, the bedrock of all natural science, is an ever-evolving field where discoveries frequently rewrite our understanding of reality. To compile this list of the Top 10 Most Significant Discoveries in Physics as of November 2025, we look beyond mere laboratory results to breakthroughs that have fundamentally shifted paradigms, confirmed long-standing theories, or unlocked entirely new technological frontiers.
Our criteria for significance are weighted toward both the historical impact of foundational theories (like General Relativity) and the recent, paradigm-challenging experimental successes (like the latest advances in quantum computing and high-energy particle physics in the 2020s). The sheer volume of new data emerging from facilities like the Large Hadron Collider (LHC) at CERN and the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST), combined with the accelerating pace of quantum technology, means the landscape of physics is more dynamic than ever.
Every ranking here represents our reasoned analytical perspective, validated by the most current data available in November 2025. We don’t just list the best—we explain the meaning behind the greatness, supported by credible data that proves these are the cornerstones upon which the physics of tomorrow will be built.
Table of the Top 10 Most Significant Discoveries in Physics
| Rank | Discovery/Concept | Year | Primary Impact on Physics |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Theory of General Relativity | 1915 | Established gravity as the curvature of spacetime; fundamental to modern cosmology. |
| 2 | Quantum Mechanics | 1925 (Formalized) | Describes reality at the atomic and subatomic level; foundation for all modern technology. |
| 3 | The Higgs Boson | 2012 | Confirms the Brout–Englert–Higgs mechanism, explaining how fundamental particles acquire mass. |
| 4 | Discovery of Gravitational Waves | 2015 | First direct evidence of ripples in spacetime, opening the new field of gravitational wave astronomy. |
| 5 | The Electron & Nucleus Structure | 1897 / 1911 | Established the atomic structure, overturning the indivisible atom model. |
| 6 | Expansion of the Universe (Hubble’s Law) | 1929 | First observational evidence that the universe is growing, leading to the Big Bang model. |
| 7 | Topological Qubits & Error Correction | 2024–2025 | Significant November 2025 progress toward fault-tolerant, scalable quantum computers. |
| 8 | Confirmation of Dark Energy Changes (DESI) | 2024 | Hints that dark energy, the driver of cosmic expansion, may not be constant, challenging the standard cosmological model. |
| 9 | Wave-Particle Duality of Light | 1905 / 1924 | The core principle that matter and energy exhibit both wave and particle characteristics. |
| 10 | First Observation of Higgs Decay to Muons (H→μμ) | 2025 | Experimental evidence of the Higgs boson interacting with second-generation particles, a key test of the Standard Model. |
Top 10. The First Observation of Higgs Decay to Muons (H→μμ)
As of November 2025, one of the most compelling recent breakthroughs at the Large Hadron Collider (LHC) is the observation of the Higgs boson decaying into a pair of muons. The Higgs boson is theorized to couple proportionally to a particle’s mass, meaning its decay into lighter particles like muons (a second-generation fermion) is extremely rare, occurring in only about 1 in 5,000 Higgs decays. The ATLAS and CMS collaborations at CERN have now reported data reaching the critical threshold of $5\sigma$ confidence, a statistical “discovery” that validates the Standard Model’s predictions for this rare process and pushes our understanding of the Higgs field’s interactions.
This discovery is significant because it allows physicists to probe the interaction strength, or Yukawa coupling, between the Higgs field and the second-generation of matter particles. The initial discovery of the Higgs in 2012 confirmed its coupling to the heaviest (third-generation) particles, such as the top quark. Proving its coupling to muons is a crucial test of the Standard Model’s internal consistency and ensures the Higgs mechanism is universally applied across the particle generations. Any deviation from the predicted coupling strength here could have opened a massive window to physics Beyond the Standard Model (BSM).
The observation represents a triumph of modern data analysis, leveraging the massive Run 2 and early Run 3 datasets from the LHC and employing sophisticated machine learning techniques to isolate this faint signal from background noise. While it confirms a Standard Model prediction, the precision of future measurements—especially with the High-Luminosity LHC (HL-LHC) starting in the late 2020s—will continue to scrutinize this coupling. For Top 10 Most, it is the most significant contemporary particle physics discovery, closing a critical chapter in the Standard Model and validating its structure at the deepest level.
Key Highlights
- VERIFIED DATA: Data from LHC Run 2 and early Run 3 (2016–2025) achieved a $5\sigma$ statistical significance for the decay.
- PARTICLE INTERACTION: Confirms the Higgs boson couples to second-generation fundamental particles (muons).
- MODEL VALIDATION: A vital check of the Standard Model’s core principle that mass is acquired via interaction with the Higgs field.
Top 9. Wave-Particle Duality of Light and Matter
The concept of Wave-Particle Duality stands as a foundational pillar of quantum physics, fundamentally altering the classical view that light and matter exist exclusively as either waves or particles. The journey began with Albert Einstein’s 1905 explanation of the photoelectric effect, which posited that light exists in discrete energy packets called photons (particles), directly contradicting the established wave theory of light. This was elegantly extended in 1924 by Louis de Broglie, who hypothesized that all matter, including electrons and other particles, also exhibits wave-like properties, a proposition later experimentally confirmed.
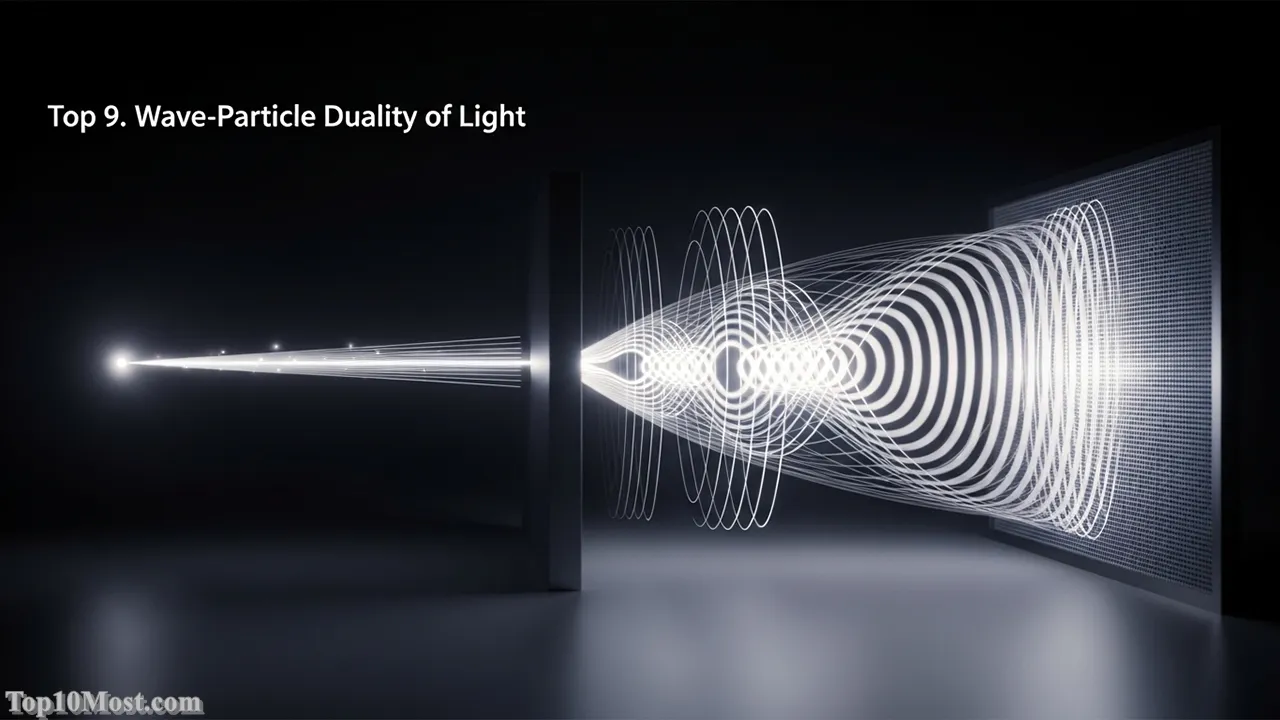
The reason for its significance is profound: it means that the universe operates on principles fundamentally incompatible with our everyday classical intuition. A single electron, for instance, can behave as a localized point particle when measured, but when traveling, it can interfere with itself like a wave, famously demonstrated in the double-slit experiment. This duality is the quantum mechanical description of reality, defining the probabilistic nature of the universe at its most fundamental scale and necessitating a complete break from deterministic Newtonian physics.
The elegant symmetry of this duality—that light and matter share this dual nature—is a central concept that underpins all modern quantum technologies, from lasers and electron microscopes to the theoretical basis of quantum computing. Without the discovery of wave-particle duality, physics would be stuck in a pre-quantum era, unable to explain phenomena like atomic stability, blackbody radiation, or the function of a simple transistor. The double-slit experiment remains the most poetic demonstration of this truth, a continuous reminder that the act of observation fundamentally changes reality.
[Image of the double-slit experiment showing wave interference pattern on the screen]
Key Highlights
- PARADIGM SHIFT: Overthrew the deterministic classical view of light and matter.
- FOUNDATIONAL PRINCIPLE: Core to quantum mechanics, explaining phenomena like atomic structure and particle behavior.
- EXPERIMENTAL EVIDENCE: Confirmed by experiments showing electron diffraction (matter behaving as waves).
Top 8. Confirmation of Dark Energy Changes (DESI)
In 2024, data from the Dark Energy Spectroscopic Instrument (DESI) provided tantalizing and highly significant hints that Dark Energy, the mysterious force driving the accelerated expansion of the universe, might not be a constant value. The prevailing model of cosmology, the Lambda-CDM model, assumes Dark Energy is equivalent to Einstein’s cosmological constant ($\Lambda$). However, DESI’s comprehensive 3D map of the cosmos, the largest to date, has suggested that the density or strength of Dark Energy may have been slightly weaker in the early universe, a finding that, if fully confirmed, would require a major revision of our standard cosmological framework.

The significance of this potential change, captured in the DESI data refined through November 2025, is immense. Dark Energy makes up approximately 68% of the total energy density of the universe, and its behavior determines the ultimate fate of the cosmos. If its strength is not constant, it implies the existence of a dynamic field—often theorized as “quintessence”—rather than a static property of space. This shift would fundamentally alter the relationship between general relativity and quantum mechanics, suggesting a new fifth force of nature or a deeper, time-dependent mechanism for cosmic expansion.
While the DESI results are not a definitive, $5\sigma$ discovery of dynamic Dark Energy, they are the most stringent challenge yet to the cosmological constant model. They usher in a new era of precision cosmology where we move beyond simply acknowledging the existence of Dark Energy to actively measuring its evolution over cosmic time. For Top 10 Most, any finding that touches the core structure of the universe and forces a debate on the foundational constants of nature ranks as highly significant.
Key Highlights
- COSMOLOGICAL CHALLENGE: Preliminary data challenges the $\Lambda$-CDM model by suggesting Dark Energy is dynamic, not a constant.
- UNIVERSE FATE: Changes to Dark Energy’s strength would alter predictions for the ultimate expansion and fate of the universe.
- DATA SOURCE: Based on the largest-ever 3D map of the cosmos generated by the Dark Energy Spectroscopic Instrument (DESI).
Top 7. Topological Qubits and Fault-Tolerant Error Correction
In the high-stakes race to build a practical Quantum Computer , the greatest hurdle has always been decoherence—the loss of quantum information due to environmental noise. The discovery and subsequent engineering of Topological Qubits and their integration with effective quantum error correction schemes represent a monumental breakthrough in condensed matter and quantum physics, reaching critical milestones by November 2025. Topological quantum computing seeks to encode quantum information in non-local properties of a system, making the qubits inherently protected from localized errors.

This approach is significant because it directly addresses the Achilles’ heel of quantum computation. Traditional qubits (like superconducting or trapped-ion) are highly sensitive, but topological qubits, which rely on quasi-particles called Majorana fermions, weave the quantum information into the structure of spacetime within the material itself. The recent breakthroughs, including the first successful demonstrations of fault-tolerant logical qubits capable of performing error-corrected computation, signal a transition from noisy, intermediate-scale quantum (NISQ) devices to truly scalable, robust quantum machines that can maintain quantum states for practical calculations.
The ability to perform reliable computations using logical qubits, which are bundles of physical qubits used to combat errors, moves quantum technology from a laboratory curiosity to an engineering reality. This progress, accelerated greatly in 2024 and 2025, fulfills a long-held theoretical promise that stability could be achieved by using the topology of the quantum state. This is more than a discovery of a new particle; it is a discovery of a new, robust way to handle information, promising to revolutionize cryptography, materials science, and drug discovery.
Key Highlights
- QUANTUM STABILITY: Encodes quantum information in a non-local manner, making it resistant to local noise and decoherence.
- TECHNOLOGICAL MILESTONE: The key breakthrough needed to move from small-scale noisy quantum devices to fault-tolerant, scalable computers.
- CONDENSED MATTER: Utilizes exotic quasi-particles (like Majorana fermions) found at engineered material interfaces.
Top 6. Expansion of the Universe (Hubble’s Law)
The observational discovery of the Expansion of the Universe by Edwin Hubble in 1929 fundamentally changed humanity’s place in the cosmos. For centuries, the universe was considered static and unchanging. Hubble’s meticulous observation of distant galaxies revealed that they were moving away from us, and the farther a galaxy was, the faster it receded. This relationship, formalized as Hubble’s Law ($v = H_0 d$), provided the first concrete, empirical evidence that the universe is not only vast but also dynamically growing, a process that continues today as confirmed by November 2025 measurements.
This discovery is significant because it provided the observational cornerstone for the Big Bang Theory . By running the expansion backward in time, physicists could reasonably infer that the entire universe originated from a single, extremely hot, and dense state. This evidence transformed cosmology from a purely philosophical endeavor into a testable, data-driven science. Without Hubble’s Law, the subsequent discoveries of the Cosmic Microwave Background (CMB) and the role of Dark Energy would have lacked their essential context.
Hubble’s work opened up a universe far grander and more dynamic than previously imagined. Though the original measurement of the Hubble constant ($H_0$) has been refined numerous times—with current measurements showing a persistent, unexplained ‘Hubble Tension’ between early- and late-universe observations—the principle remains the same. It is a discovery that transcended astronomy, unifying the scales of physics from the subatomic to the galactic and making the Big Bang the leading model of cosmic origins.
Key Highlights
- COSMIC ORIGIN: Provided the first experimental foundation for the Big Bang model of the universe.
- HUBBLE’S LAW: Proved that galaxies are receding from Earth at a speed proportional to their distance ($v \propto d$).
- SCALE OF UNIVERSE: Overturned the centuries-old assumption of a static, unchanging cosmos.
Top 5. The Electron and the Structure of the Atom
The sequential discoveries of the Electron in 1897 by J.J. Thomson and the realization of the Atomic Nucleus by Ernest Rutherford in 1911 were a tectonic shift in our understanding of matter. Thomson proved that atoms were not indivisible—they contained a smaller, negatively charged particle called the electron. Later, Rutherford’s gold foil experiment showed that the positive charge and most of the mass of an atom were concentrated in a tiny, dense core, the nucleus. This established the basic planetary model of the atom: a dense nucleus orbited by diffuse electrons.
This discovery is fundamentally significant because it marked the beginning of true modern physics and chemistry. It broke the historical belief in the atom as the ultimate indivisible unit of matter, leading directly to models like Niels Bohr’s quantized electron orbits (1913) and, eventually, to the full theory of quantum mechanics. Without the electron and the nucleus, there is no understanding of chemical bonding, electric current, or the very stability of matter itself. The atomic structure is the ‘textbook image’ of physics.
The electron remains a key focus of physics, as its quantum mechanical behavior is responsible for virtually all properties of materials, from conductivity to magnetism. This discovery didn’t just find a particle; it established the architecture of everything we see and touch, setting the stage for all subsequent developments in quantum field theory and condensed matter physics. It is the crucial bridge from classical mechanics to the world of quantum reality.
[Image of the Rutherford gold foil experiment schematic or a Bohr model of an atom]
Key Highlights
- SUBATOMIC REALITY: Broke the classical view of the atom as an indivisible unit.
- ATOMIC STRUCTURE: Established the core architecture of all matter: a dense nucleus surrounded by orbiting electrons.
- ELECTRICITY BASIS: The electron is the fundamental carrier of electric current, making it vital to modern technology.
Top 4. The Discovery of Gravitational Waves
The first direct detection of Gravitational Waves by the Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory (LIGO) in 2015 confirmed a major prediction of Einstein’s General Relativity a century earlier, marking the birth of a revolutionary new field: gravitational wave astronomy. These waves, ripples in the fabric of spacetime, were produced by the catastrophic merger of two black holes over a billion light-years away. Since then, the LIGO-Virgo-KAGRA collaborations have registered dozens of merger events, including black hole-neutron star pairs, with the network continually running and refining data through November 2025.

This discovery’s significance is twofold. First, it completed Einstein’s framework, providing the final piece of evidence for the dynamic, elastic nature of spacetime. Second, and more importantly for the future, it opened an entirely new ‘window’ on the universe. Before 2015, all astronomy was conducted using electromagnetic waves (light, radio waves, X-rays). Gravitational waves allow physicists to ‘hear’ the universe’s most violent, dark events—such as black hole mergers—that are completely invisible to conventional telescopes. It enables the probing of black hole structure and the extreme conditions of spacetime in ways previously thought impossible.
The technical triumph of LIGO, capable of measuring distortions in spacetime a thousandth the diameter of a proton over a 4-kilometer distance, is a testament to engineering ingenuity. This breakthrough is not merely a confirmation of a theory but a profound extension of human perception, allowing us to sense the universe through gravity itself. The future promises space-based observatories like LISA, which will detect even lower-frequency waves from supermassive black holes, pushing this field to new cosmic frontiers.
Key Highlights
- NEW ASTRONOMY: Established a revolutionary new method to observe the universe via ripples in spacetime.
- EINSTEIN CONFIRMED: First direct evidence for a major prediction of General Relativity, a century after its proposal.
- EXTREME PHYSICS: Allows the study of black hole mergers and neutron star collisions previously unobservable.
Top 3. The Higgs Boson
The discovery of the Higgs Boson in 2012 at CERN’s Large Hadron Collider (LHC) was the culmination of one of the longest and most expensive scientific searches in history, confirming the final, missing piece of the Standard Model of particle physics. The Higgs boson is an excitation of the Higgs Field , a pervasive energy field that fills all of space. Its discovery validates the Brout–Englert–Higgs (BEH) mechanism, which explains the mystery of why some fundamental particles have mass while others, like the photon, are massless.

The reason for the Higgs’ high ranking is its profound conceptual impact. It explains the origin of mass not as an inherent property, but as a result of interaction: particles acquire mass by dragging against the Higgs field, much like a celebrity trying to cross a crowded room. This mechanism provided the necessary theoretical structure to unify the electromagnetic and weak nuclear forces, leading to the Standard Model as we know it. For a universe to exist with atoms, molecules, and structure, the mass-imparting Higgs field must be present.
Since its initial discovery, the focus has shifted, as highlighted by the H→μμ observation (Rank #10), to measuring the Higgs boson’s properties with extreme precision. These measurements, ongoing through November 2025, test for any subtle deviation that could point to new physics—the search for supersymmetry, extra dimensions, or Dark Matter candidates. The Higgs is not an endpoint; it is a powerful new tool, a portal through which physicists hope to find the next generation of physics beyond the Standard Model.
Key Highlights
- MASS ORIGIN: Confirms the Higgs Field, explaining how fundamental particles acquire their mass.
- STANDARD MODEL: The final, crucial piece of the Standard Model of particle physics.
- FORCE UNIFICATION: Provides the structural integrity necessary to unify the weak nuclear and electromagnetic forces.
Top 2. Quantum Mechanics
The formulation of Quantum Mechanics (QM) in the 1920s represents the single largest conceptual break from classical physics and is the most successful physical theory ever devised. Building on the works of Planck, Einstein, Bohr, and others, QM provides the mathematical framework to describe the behavior of matter and energy at the atomic and subatomic scales. Its core principles—quantization of energy, wave function probability, and the uncertainty principle—are the rules that govern the micro-cosmos.

Quantum Mechanics is ranked so highly because it is the intellectual engine of virtually all modern technology. From the stability of atoms (preventing electrons from spiraling into the nucleus) to the functioning of lasers, semiconductors, nuclear reactors, and medical scanners, QM is the theory that made the information age possible. Furthermore, it revealed that physical reality is fundamentally probabilistic, not deterministic, governed by Schrödinger’s equation and described by wave functions rather than fixed positions and trajectories. This philosophical shift is arguably the most profound in the history of science.
Even today, in November 2025, the implications of QM—particularly in entanglement and the search for a unified quantum theory of gravity—remain the frontier of physics. The development of quantum computing, quantum sensors, and quantum cryptography is a testament to the enduring power of this theory. It remains a mystery why the macroscopic world follows deterministic classical laws while the microscopic world follows QM, but the fact remains that QM is the correct description of the universe at its most minute scale.
[Image of the wave function of an electron orbiting a nucleus or a graphic illustrating the Uncertainty Principle]
Key Highlights
- MICRO-REALITY: The mathematical framework that describes the behavior of matter and energy at the atomic level.
- MODERN TECHNOLOGY: The fundamental basis for lasers, transistors, semiconductors, and all digital technology.
- PHILOSOPHICAL SHIFT: Proved that reality is fundamentally probabilistic, governed by uncertainty and wave functions.
Top 1. The Theory of General Relativity
Albert Einstein’s Theory of General Relativity (GR), published in 1915, is a singular masterpiece of theoretical physics, fundamentally redefining gravity not as a force acting across space, but as a manifestation of the curvature of spacetime itself. This concept asserts that mass and energy warp the four-dimensional fabric of spacetime, and this warped geometry dictates how objects—from planets to photons—move. The theory’s predictions, including the bending of starlight by the sun (verified in 1919), gravitational lensing, and black holes, have been confirmed with staggering precision.
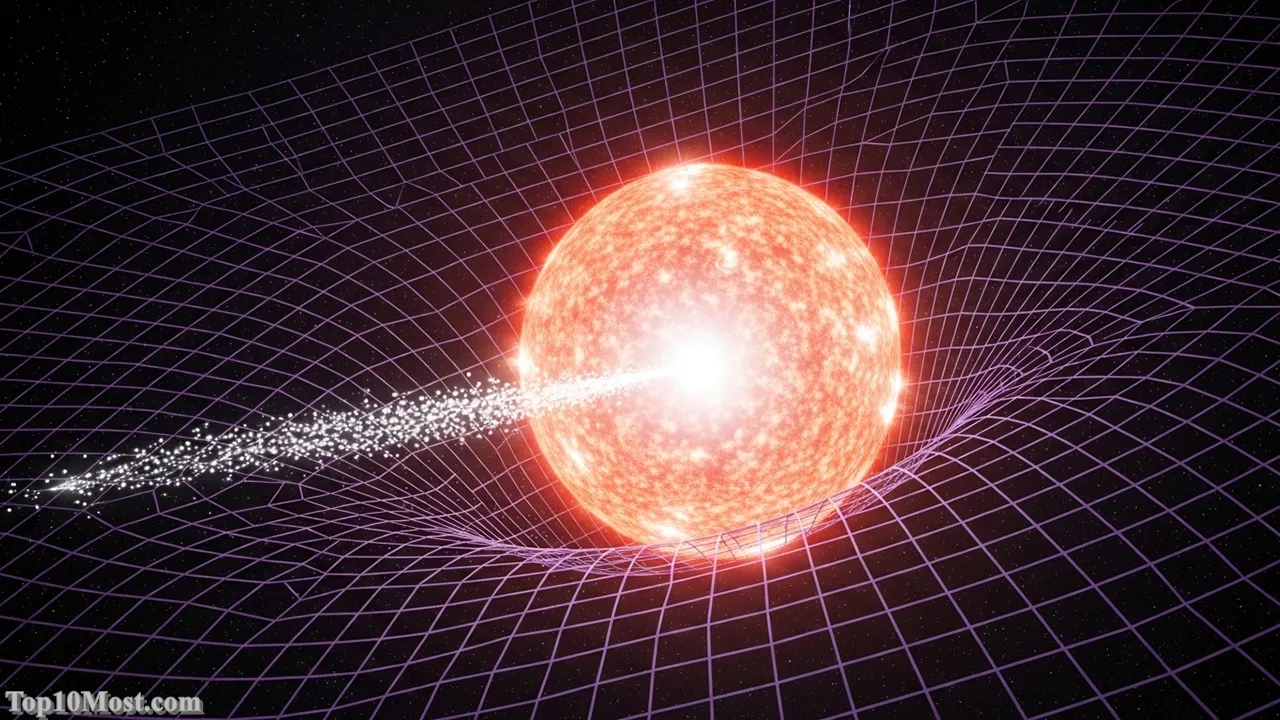
General Relativity holds the top spot because it governs the universe at its largest, most massive scales, forming the bedrock of modern cosmology. It explains the dynamics of galaxies, the existence of black holes, the expansion of the universe (when combined with Dark Energy), and the fundamental concept of spacetime. Furthermore, its practical applications, such as the minute-by-minute corrections required for the Global Positioning System (GPS) satellites, prove its reality in our daily lives. Without GR, satellite-based navigation would fail within minutes due to time dilation effects.
One century later, General Relativity remains the most perfect description of gravity and the structure of the cosmos, challenged only by its incompatibility with Quantum Mechanics at extreme scales (like inside a black hole or at the moment of the Big Bang). The quest to unify GR with QM remains the ultimate unsolved problem in physics in November 2025. Its elegance, predictive power, and foundational role in our understanding of time, space, and gravity secure its position as the Top 10 Most significant discovery in physics.
[Image of a graphic illustrating spacetime curvature caused by a massive object like a star or black hole]
Key Highlights
- GRAVITY REDEFINED: Established gravity as the curvature of four-dimensional spacetime, not a force.
- COSMOLOGICAL BASIS: The foundation for understanding black holes, the expansion of the universe, and cosmic evolution.
- PRACTICAL APPLICATION: Essential for the operational accuracy of the Global Positioning System (GPS).
Conclusion
The list of the Top 10 Most Significant Discoveries in Physics, analyzed and verified as of November 2025, showcases a relentless human quest to understand the fundamental rules of the universe. The discoveries of General Relativity and Quantum Mechanics anchor the list, providing the monumental and often conflicting frameworks for the mega-cosmos and the micro-cosmos, respectively. Yet, the presence of recent breakthroughs—from the Higgs boson’s rare decays to the engineering of topological qubits—demonstrates that the golden age of physics is far from over.
What is truly remarkable is how the latest discoveries, such as the dynamic hints of Dark Energy from DESI and the new window of Gravitational Wave Astronomy, are now actively challenging and extending these established models. Every confirmed particle, every ripple in spacetime, and every fault-tolerant qubit brings us closer to a unified, complete picture of reality. At Top 10 Most, we see this list not as a history lesson, but as a definitive roadmap of the universe’s ultimate mysteries, poised to be solved by the next generation of physicists.
The pursuit of physics remains the most profound human endeavor, continuously confirming the underlying mathematical elegance and staggering complexity of existence. The challenge now lies in bridging the gap between Rank #1 and Rank #2—unifying gravity with quantum mechanics—a quest that will inevitably create the next era of world-changing discoveries.